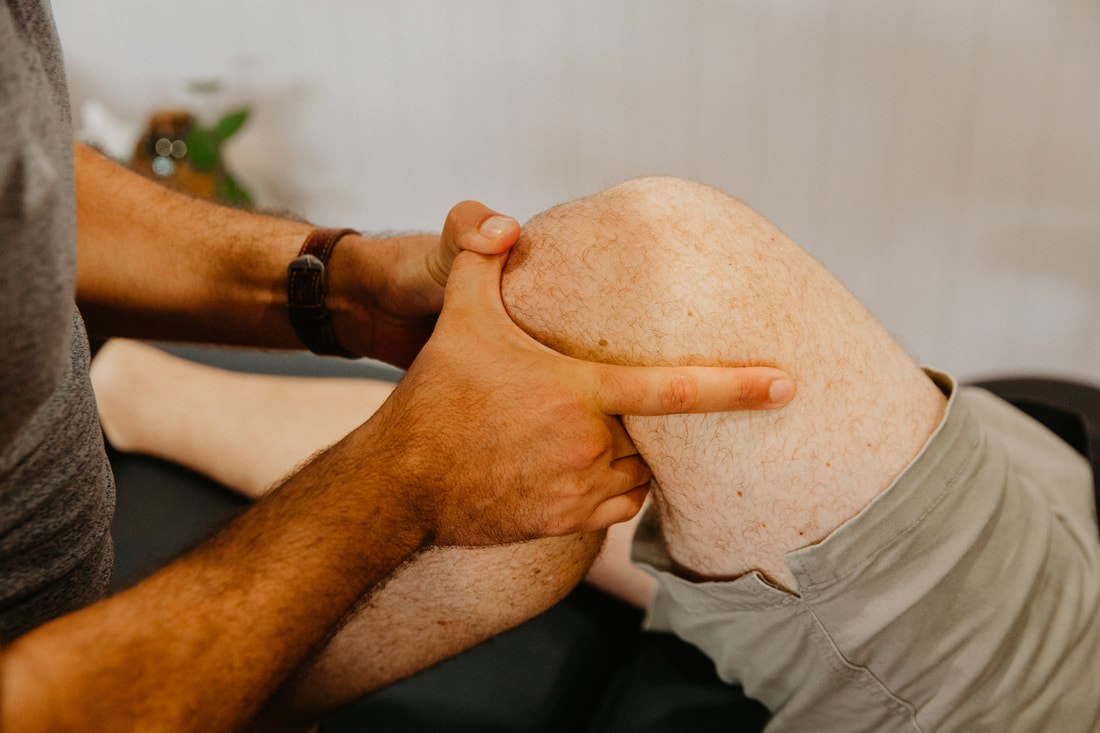
Chondromalacia patella physiotherapy Brisbane southside.
What is Chondromalacia Patella?
Chondromalacia Patella, also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome, is a common knee condition that causes pain and discomfort around the kneecap. It occurs when the cartilage on the undersurface of the kneecap (patella) becomes damaged or soft, leading to inflammation and pain.
What is the difference between Chondromalacia Patella and patellofemoral pain syndrome?
Chondromalacia Patella and patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) are two terms that are often used interchangeably to describe a similar condition that causes pain in the front of the knee. However, there are some differences between the two terms.
Chondromalacia Patella specifically refers to the softening or damage of the cartilage on the undersurface of the kneecap (patella). It is a more specific diagnosis and implies a structural change in the kneecap cartilage.
On the other hand, PFPS is a broader term that encompasses various conditions that cause pain around the kneecap, including Chondromalacia Patella. PFPS describes a collection of symptoms, rather than a specific structural abnormality. It refers to pain experienced in the area around the patella, which can be caused by a variety of underlying issues such as muscle weakness, imbalanced movement patterns, or abnormal joint alignment.
In summary, while Chondromalacia Patella is a specific diagnosis that describes the softening or damage of the kneecap cartilage, patellofemoral pain syndrome is a more general term that refers to a range of conditions that can cause pain in the front of the knee, including Chondromalacia Patella.
How is Chondromalacia Patella diagnosed?
Chondromalacia Patella can be diagnosed through a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. The physiotherapist will assess the patient's knee joint for tenderness, swelling, and pain. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI or ultrasound may also be ordered to rule out other conditions.
How can physiotherapy help after Chondromalacia Patella diagnosis?
Physiotherapy plays an essential role in the management of Chondromalacia Patella. The physiotherapist will develop an individualised treatment plan based on the patient's condition and symptoms. The aim of physiotherapy treatment is to reduce pain, improve knee function, and prevent further injury. The treatment may include:
How can clinical Pilates help with Chondromalacia Patella?
Clinical Pilates is a form of exercise that focuses on improving core strength, stability, and balance. Clinical Pilates can be beneficial in the management of Chondromalacia Patella by:
How can you prevent Chondromalacia Patella?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent Chondromalacia Patella, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition. Here are some prevention tips:
By following these prevention tips, you can reduce your risk of developing Chondromalacia Patella and other knee-related injuries.
What is the prognosis for Chondromalacia Patella?
The prognosis for Chondromalacia Patella varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's response to treatment. In most cases, Chondromalacia Patella is a self-limiting condition, meaning that it tends to improve with time and appropriate treatment.
For mild cases of Chondromalacia Patella, rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications may be sufficient to manage symptoms and allow the condition to heal on its own. Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve knee mechanics may also be beneficial.
For more severe cases of Chondromalacia Patella, surgery may be required to remove damaged cartilage or to realign the patella. However, surgery is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative treatment measures.
In general, the majority of individuals with Chondromalacia Patella can achieve full recovery with appropriate treatment and rehabilitation. However, some individuals may experience long-term knee pain or weakness, especially if the condition is not properly managed or if there are underlying structural abnormalities.
It is important to note that prevention and early intervention are key in managing Chondromalacia Patella. By taking steps to reduce your risk of knee injury and seeking medical attention if you experience knee pain or swelling, you can increase your chances of a positive prognosis.
If you a looking for a physiotherapist who treats Chondromalacia Patella in Brisbane we would love to help you! Our Tarragindi physiotherapy team are able to find a treatment plan to help get you moving again.
Call our friendly clinic a call on 07 3706 3407, email [email protected] or make your initial appointment booking via the link below.
Chondromalacia Patella, also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome, is a common knee condition that causes pain and discomfort around the kneecap. It occurs when the cartilage on the undersurface of the kneecap (patella) becomes damaged or soft, leading to inflammation and pain.
What is the difference between Chondromalacia Patella and patellofemoral pain syndrome?
Chondromalacia Patella and patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) are two terms that are often used interchangeably to describe a similar condition that causes pain in the front of the knee. However, there are some differences between the two terms.
Chondromalacia Patella specifically refers to the softening or damage of the cartilage on the undersurface of the kneecap (patella). It is a more specific diagnosis and implies a structural change in the kneecap cartilage.
On the other hand, PFPS is a broader term that encompasses various conditions that cause pain around the kneecap, including Chondromalacia Patella. PFPS describes a collection of symptoms, rather than a specific structural abnormality. It refers to pain experienced in the area around the patella, which can be caused by a variety of underlying issues such as muscle weakness, imbalanced movement patterns, or abnormal joint alignment.
In summary, while Chondromalacia Patella is a specific diagnosis that describes the softening or damage of the kneecap cartilage, patellofemoral pain syndrome is a more general term that refers to a range of conditions that can cause pain in the front of the knee, including Chondromalacia Patella.
How is Chondromalacia Patella diagnosed?
Chondromalacia Patella can be diagnosed through a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. The physiotherapist will assess the patient's knee joint for tenderness, swelling, and pain. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI or ultrasound may also be ordered to rule out other conditions.
How can physiotherapy help after Chondromalacia Patella diagnosis?
Physiotherapy plays an essential role in the management of Chondromalacia Patella. The physiotherapist will develop an individualised treatment plan based on the patient's condition and symptoms. The aim of physiotherapy treatment is to reduce pain, improve knee function, and prevent further injury. The treatment may include:
- Strengthening exercises: The physiotherapist will prescribe exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Strong muscles help to stabilise the knee joint and reduce stress on the kneecap.
- Stretching exercises: The physiotherapist will prescribe exercises to improve flexibility and range of motion in the knee joint.
- Manual therapy: The physiotherapist may use manual techniques such as massage, joint mobilisation, or manipulation to reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Taping or bracing: Taping or bracing may be used to provide support to the knee joint and reduce stress on the kneecap.
How can clinical Pilates help with Chondromalacia Patella?
Clinical Pilates is a form of exercise that focuses on improving core strength, stability, and balance. Clinical Pilates can be beneficial in the management of Chondromalacia Patella by:
- Strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Improving core strength and stability, which helps to support the knee joint and reduce stress on the kneecap.
- Improving balance and coordination, which can help to prevent falls and further injury.
How can you prevent Chondromalacia Patella?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent Chondromalacia Patella, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition. Here are some prevention tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the stress on your knees, including your kneecap, and increase your risk of developing Chondromalacia Patella. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the amount of stress placed on your knees and help prevent knee pain and injury.
- Wear proper footwear: Wearing supportive and well-fitted shoes can help to reduce the impact on your knees when you walk, run or exercise. You can also use shoe inserts or orthotics to provide extra support to your feet and knees.
- Avoid activities that put excessive stress on your knees: High-impact activities such as running, jumping, or sudden changes of direction can put excessive stress on your knees and increase your risk of developing knee pain or injury. Consider low-impact activities like swimming or cycling instead.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise: Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or duration of exercise, which can put undue stress on your knees. Gradually build up the intensity and duration of your exercise routine to give your body time to adjust.
- Use proper form and technique when exercising: Using proper form and technique when performing exercises can help to reduce the risk of injury. For example, when squatting, ensure your knees do not collapse inwards and are over your feet rather than in front of them.
- Strengthen your muscles: Weakness in the muscles that support your knee joint can increase your risk of developing Chondromalacia Patella. Strengthening exercises for the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes can help to improve the stability of your knee joint and reduce the risk of injury.
By following these prevention tips, you can reduce your risk of developing Chondromalacia Patella and other knee-related injuries.
What is the prognosis for Chondromalacia Patella?
The prognosis for Chondromalacia Patella varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's response to treatment. In most cases, Chondromalacia Patella is a self-limiting condition, meaning that it tends to improve with time and appropriate treatment.
For mild cases of Chondromalacia Patella, rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications may be sufficient to manage symptoms and allow the condition to heal on its own. Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve knee mechanics may also be beneficial.
For more severe cases of Chondromalacia Patella, surgery may be required to remove damaged cartilage or to realign the patella. However, surgery is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative treatment measures.
In general, the majority of individuals with Chondromalacia Patella can achieve full recovery with appropriate treatment and rehabilitation. However, some individuals may experience long-term knee pain or weakness, especially if the condition is not properly managed or if there are underlying structural abnormalities.
It is important to note that prevention and early intervention are key in managing Chondromalacia Patella. By taking steps to reduce your risk of knee injury and seeking medical attention if you experience knee pain or swelling, you can increase your chances of a positive prognosis.
If you a looking for a physiotherapist who treats Chondromalacia Patella in Brisbane we would love to help you! Our Tarragindi physiotherapy team are able to find a treatment plan to help get you moving again.
Call our friendly clinic a call on 07 3706 3407, email [email protected] or make your initial appointment booking via the link below.
Who to book in with:
Mauricio Bara
|
|