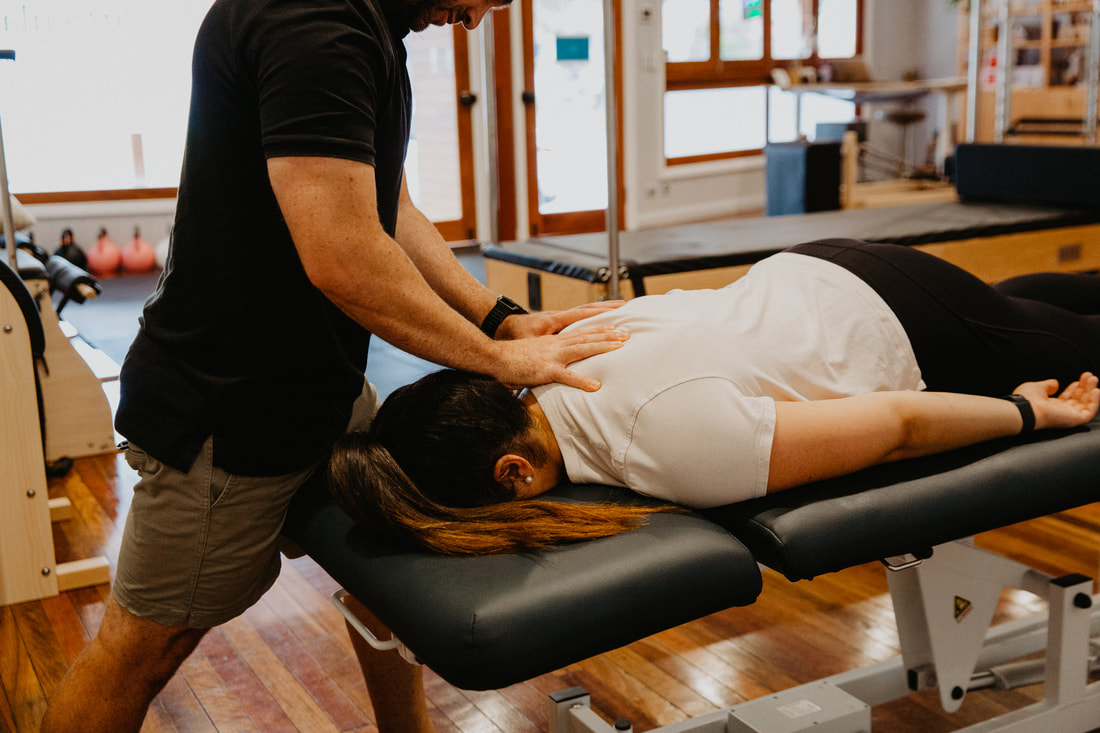
Degenerative Disc Disease Physiotherapy Brisbane southside.
What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
Degenerative disc disease occurs when the discs that separate the vertebrae in the spine deteriorate or degenerate over time. These discs are soft, rubbery cushions that provide shock absorption and allow for flexibility in the spine. As they wear down, they may lead to various spinal problems and discomfort.
What causes Degenerative Disc Disease?
The primary cause of degenerative disc disease is the natural aging process. However, several factors can contribute to its development or exacerbate its symptoms, including:
What are the symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease?
The symptoms of degenerative disc disease can vary from person to person. Common signs and symptoms include:
How is Degenerative Disc Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing degenerative disc disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms and conduct tests to determine the extent of disc degeneration and rule out other possible causes of your pain.
How is Degenerative Disc Disease treated?
Treatment for degenerative disc disease aims to manage pain and improve function. It often includes a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, surgical interventions. Common treatment options include:
How can physiotherapy help with Degenerative Disc Disease?
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, can play a significant role in helping individuals with degenerative disc disease (DDD) manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and potentially delay the progression of the condition. Here's how physiotherapy can be beneficial for individuals with DDD:
If you or a loved one has questions about Degenerative Disc Disease and how our physiotherapists might be able to help please call us on 07 3706 3407 or email [email protected]. We would love to work with you!
Degenerative disc disease occurs when the discs that separate the vertebrae in the spine deteriorate or degenerate over time. These discs are soft, rubbery cushions that provide shock absorption and allow for flexibility in the spine. As they wear down, they may lead to various spinal problems and discomfort.
What causes Degenerative Disc Disease?
The primary cause of degenerative disc disease is the natural aging process. However, several factors can contribute to its development or exacerbate its symptoms, including:
- Age: DDD becomes more common as people get older, typically starting in the late 30s to early 40s.
- Genetics: A family history of DDD can increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors like smoking, excessive weight, and poor nutrition can accelerate disc degeneration.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the spine can initiate or worsen DDD.
What are the symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease?
The symptoms of degenerative disc disease can vary from person to person. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Back Pain: Persistent and often chronic pain in the lower back or neck.
- Pain Radiation: Pain that may radiate into the buttocks, legs (sciatica), or arms, depending on the location of the affected discs.
- Numbness and Tingling: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities.
- Pain Aggravation: Pain that worsens with activities like bending, lifting, or twisting.
- Pain Relief: Pain that may improve with rest or changes in body position.
How is Degenerative Disc Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing degenerative disc disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms and conduct tests to determine the extent of disc degeneration and rule out other possible causes of your pain.
How is Degenerative Disc Disease treated?
Treatment for degenerative disc disease aims to manage pain and improve function. It often includes a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, surgical interventions. Common treatment options include:
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the back and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants may be prescribed.
- Epidural Injections: Steroid injections into the spine to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight management, smoking cessation, and proper body mechanics can help alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: Surgical options, such as spinal fusion or disc replacement, may be considered for severe cases when conservative treatments are ineffective.
How can physiotherapy help with Degenerative Disc Disease?
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, can play a significant role in helping individuals with degenerative disc disease (DDD) manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and potentially delay the progression of the condition. Here's how physiotherapy can be beneficial for individuals with DDD:
- Pain Management: Physiotherapists can use various techniques to help alleviate pain associated with DDD. These may include manual therapy, such as joint mobilisation and soft tissue massage, to reduce muscle tension and improve joint mobility.
- Strengthening Exercises: Physiotherapists design exercise programs tailored to the individual's specific needs and limitations. Strengthening exercises can target the muscles that support the spine, helping to stabilise the affected area and reduce stress on the degenerated discs.
- Flexibility and Range of Motion: Physiotherapy can help improve spinal flexibility and range of motion through stretching exercises and gentle spinal mobilisation techniques. Increased flexibility can enhance overall spinal function and reduce pain.
- Posture and Body Mechanics: Physiotherapists can educate patients on proper body mechanics and ergonomics to prevent exacerbation of DDD symptoms. This includes guidance on how to sit, stand, lift, and perform daily activities without putting excessive strain on the spine.
- Core Strengthening: Strengthening the core muscles, including the abdominal and lower back muscles, can provide better support to the spine. A strong core can help distribute the load more evenly across the spine and reduce stress on degenerated discs.
- Pain Modalities: Physiotherapists may use modalities such as heat, cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area.
- Education: Patients receive education about their condition and how to manage it effectively. This includes advice on lifestyle modifications, such as weight management and smoking cessation, which can impact DDD.
- Functional Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy aims to improve patients' ability to perform daily activities with less pain and discomfort. This can enhance their overall quality of life and independence.
- Prevention: Physiotherapists can provide guidance on injury prevention strategies and techniques to reduce the risk of exacerbating DDD.
- Patient-Centered Care: Physiotherapy treatment plans are individualised to each patient's specific needs and goals. This personalised approach ensures that the therapy is tailored to address the unique challenges and symptoms of the individual with DDD.
If you or a loved one has questions about Degenerative Disc Disease and how our physiotherapists might be able to help please call us on 07 3706 3407 or email [email protected]. We would love to work with you!
Who to book in with:
Yulia Khasyanova
|
Mauricio Bara
|
Monica Hanna
|